Plastic pellets, commonly referred to as nurdles, are often overlooked yet crucial components of modern manufacturing, serving as the primary source of numerous products we interact with on a daily basis. From the packaging that secures our goods to the actual components in electronics, they lie at the heart of it all. But have you ever considered how those tiny little pellets are converted into objects of daily use”? This article will examine the multifaceted applications of plastic pellets and their crucial role in various industries, including automotive and healthcare. Either curiosity about science or concern for the environment will stir within you; this handy guide has it all. Gear up to explore how plastic pellets impact the world- a few of which you might have never even imagined!
The Basics of Plastic Pellets

What Are Plastic Pellets?
Plastic pellets, also known as resin pellets or polymer granules, are a basic raw material used extensively for the production of plastic products. These tiny, bead-like materials are prepared from synthetic polymers like polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene, and polyvinyl chloride. With their uniform shape and size, these pellets are easier to melt, mold, and process into forms and thus make up hundreds of plastic items.
The plastic pellets from which a great variety of products are formed are used all over the world in industries such as packaging, automobile, building, and electronics for their versatility, durability, and relative cheapness. The production of plastic pellets worldwide has grown exponentially, with millions of tonnes produced annually to meet the demand for lightweight and durable goods. Keeping pace with developments in polymer technologies, these advancements lead to the creation of specialized pellets that include biodegradable and recycled options, helping industries follow a sustainable path. These conscious moves demonstrate that plastic pellets remain one of the major players in the current manufacturing industry.
Type of Plastic Pellets
The plastic pellets, available in a wide variety of types, have been designed to suit special applications based on their physical and chemical properties. Here are a few common categories:
Polyethylene (PE) Pellets: These are the most widely produced types of plastic, classified into two categories: high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and low-density polyethylene (LDPE). HDPE pellets are used for applications that require high rigidity and strength, such as pipes and containers. In contrast, LDPE pellets are commonly used for flexible packaging materials, such as plastic bags and films.
Polypropylene (PP) Pellets: Polypropylene pellets are the ideal choice for automotive parts, medical devices, and food-safe containers due to their toughness and resistance to heat and chemicals. Being lightweight and versatile, they’re preferred in many industrial domains.
Polystyrene (PS) Pellets: Polystyrene pellets are available in two forms: solid and foam. Solid PS is used in cutlery, CD cases, and housings for appliances, whereas expanded polystyrene (EPS) is a lightweight construct primarily used for packaging and insulation.
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Pellets: These PVC pellets are versatile and find numerous applications. The rigid variety is considered an adult material in construction, particularly in pipes and window frames, while flexible PVC is used for hoses, cables, and synthetic leather.
Biodegradable Plastic Pellets: With a major spotlight geared on environmental sustainability, pellets made from substances such as polylactic acid (PLA) and polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) are gaining significance. These pellets break down more readily in natural environments, thereby reducing long-term pollution.
Recycled Plastic Pellets: These pellets are made from waste originating from either post-consumer or post-industrial plastic. These are processed and refined to produce a high-quality material suitable for various applications, including textiles, construction materials, and packaging.
The making and uses of these different types of plastic pellets are articulate enough to highlight the versatility of the material, catering to various industries. Additionally, the availability of eco-conscious options, such as biodegradable and recycled pellets, appears to be very appealing, if not encouraging, for transitioning to more responsible production.
How Plastic Pellets are Produced
The production of plastic pellets begins with the extraction and refining of raw materials, primarily derived from crude oil and natural gas. These hydrocarbons undergo cracking; large molecules are broken down into smaller molecules, such as ethylene and propylene, which are used as building blocks for various types of plastics. These monomers are polymerized into resins, which are long-chain molecules that serve as the base for the plastic.
After polymer resins are produced, they are melted and blended with additives such as stabilizers, colorants, and fillers to impart more desirable properties like durability, flexibility, or UV resistance. The molten polymer mixture is introduced into the extrusion machine, where it is formed into two to three thin, continuous strands. The strands are chilled, typically in a water bath, and then cut into tiny, uniform pellets.
A primary factor in quality control stands throughout the manufacturing process, in which great importance is attached to package size, shape, and chemical composition. Various contemporary production methods incorporate sustainable practices and energy sources, such as recycling scrap materials and reducing waste, which minimize adverse environmental impacts. This is in the spirit of advancing a greener environment and tackling the ever-changing demands placed on them by worldwide markets.
Applications of Plastic Pellets

Uses of Plastic Pellets in Manufacturing
Plastics, the diverse industries-These industries, in turn, manufacture several types of products from the raw materials. One of the most significant uses is in the manufacturing of plastic packaging, including bottles, containers, and flexible films, which are necessary for ensuring the safe packaging and transfer of products. Plastic pellets are manufactured in the automotive industry to produce lightweight solid components, such as bumper systems, dashboards, and interior trims, which improve fuel efficiency and vehicle performance.
The plastic pellets are also widely used in construction, primarily for pipes, insulation panels, and roofing membranes, among other applications, due to their versatility, resistance to weathering, and economic benefits. Then, the electronics industry makes heavy use of plastic pellets for the injection molding of casings, connectors, and circuit insulation to ensure the level of durability and safety required by a host of devices.
Recent trends highlight the growing use of bioplastics and recycled pellets as a response to the demand for greener alternatives. These materials are at the heart of achieving a low environmental impact while maintaining a high level of performance. With the support of new technologies, such as precision molding and additive manufacturing, even further applications of plastic pellets will be developed, with ongoing innovation spanning from agricultural to consumer goods.
Plastic Products Made from Pellets
Plastic pellets serve as the backbone in the manufacturing of various products that pervade modern life. From everyday household items, such as food containers and packaging materials, to sophisticated engineering components, each industry’s functioning depends on these versatile materials. For instance, injection molding processes utilize these pellets to manufacture durable components, including automotive parts, medical devices, and electronic casings. Recent developments in bioplastics have provided us with ocean-friendly products, including biodegradable cutlery, bags, and films for packaging, thereby satisfying sustainability objectives.
More importantly, industries that utilize recycled plastic pellets contribute significantly to reducing waste. This usage involves manufacturing textile fibers, outdoor furniture, and construction materials, such as pipes and insulation panels. According to recent industry data, the global recycled plastic market is steadily growing. This growth is a testament to the increasing demand for sustainable solutions at both the consumer and corporate levels. Innovations can be driven and environmental crises tackled by expanding the scope of uses of both virgin and recycled plastic pellets.
Innovative Applications Across Several Industries
The application of plastic pellets, both virgin and recycled, has led to trailblazing applications in several industries. In the automotive sector, for instance, these materials are used in the manufacture of lightweight components, which reduces the overall weight of the vehicle and, consequently, increases fuel efficiency. With the advent of advanced manufacturing methods, the environmentally friendly production of car interiors, bumpers, and dashboards from recycled plastic pellets is now a reality.
The construction industry is also finding new applications for recycled plastics in the manufacture of modular building blocks and for sustainable insulation. These materials continue to provide resilience and durability whilst now requiring little from traditional, more resource-intensive materials. On the contrary, there has been a significant rise in 3D-printing applications, where pellets are processed into filament materials to create highly complex, customized designs for both prototyping and end-use parts.
The packaging industry is further anticipating a significant revolution in the evolution of flexible packaging, innovatively employing plastic pellet technology to achieve better product protection and a reduction in raw material usage. This effort supports resource conservation while also contributing to the global effort against plastic waste. Together, these application areas highlight the dynamic role that plastic pellets play in advancing technology while addressing critical environmental concerns.
The Role of Recycled Plastic Pellets

Benefits of Using Recycled Pellets
The use of recycled pellets brings several benefits that contribute to reducing the environmental impact and enhancing industrial capacity. Primarily, the demand for virgin plastic production is significantly reduced when recycled pellets are used in products, thereby conserving natural resources, such as petroleum, and also resulting in reduced greenhouse gas emissions. Hence, industries can limit their carbon emissions by using recycled pellets while simultaneously supporting the principles of the circular economy.
In addition, recycled pellets are cost-effective; they present companies with an eco-friendly option, which may often result in a lower material cost. Through modern recycling operations, the pellets have achieved quality and consistency standards that enable them to be used in various applications, including packaging, textiles, and construction materials. Additionally, their widespread usage is another significant advantage; being easily moldable or formable means that recycled pellets are indeed the primary raw material driving many acts of modernization in industry.
Incorporating recycled pellets would enable the company to enhance its operational efficiency while enhancing its brand reputation and market competitiveness by meeting the demand of conscious consumers for environmentally friendly products. Based on these benefits, recycled pellets will take center stage in envisioning a sustainable future for industries worldwide.
Post-Consumer Recycled Plastic Pellets
Post-consumer recycled plastic pellets effectively address the global plastic waste crisis sustainably and efficiently. They are recycled pellets manufactured from materials that have served their original purpose, such as water bottles, packaging materials, and others of their kind, which are discarded into the environment. By embracing post-consumer recycled materials, industries greatly minimize plastic waste in landfills and toxicants in the ambient air.
Among the advantages of using these recycled pellets is the reduction in the production process at the factory by utilizing activated carbon. For instance, processing energy is significantly reduced when plastic is recycled rather than when it is made from virgin materials. Additionally, the pellets meet high standards of quality and merit, distinguishing them in the packaging, construction, and automotive industries. Recent recycling innovations have, in turn, supported better sorting and processing, thereby allowing post-consumer recycled plastics to be used in craft products that can now compete equally with virgin plastics in terms of durability and efficiency.
To cite the fact that reversing the perspective of using post-consumer recycled plastic pellets is an economical choice and an imperative approach toward a circular economy. By lessening the dependence on finite resources and putting a circular reuse cycle in place, companies are greenwashing sustainability globally and meeting the present demand for green drops of eco-conscious products.”
Challenges in Recycling Plastic Pellets
While recycling plastic pellets presents several technical, economic, and logistical hurdles that hinder the proper reuse of the material, the most practical considerations lie in contamination in waste streams and plastics. When differently treated or considered plastics are mixed or combined with non-plastic materials, the worst outcome is a considerable increase in difficulty for separation and reprocessing. Such contamination practically lowers the quality of the manufactured recycled pellets, thereby reducing their scope of applicability.
The second significant challenge is the energy intensity associated with the recycling operation. These energy consumption ratings involve sorting, cleaning, melting, and reshaping plastic materials; such energy-intensive procedures will ultimately drive increasing operational costs, especially in areas where renewable energy resource bases are limited. Confusion is also created by the lack of standardization in recycling processes across geographies and industries, which affects the quality of recycled materials.
Economic aspects form a principle besides the untreated. Virgin plastics are usually cheaper to manufacture as compared to recycled ones due to the fluctuating price of crude oil and gas, the raw materials for plastics. This price difference would deter many companies from investing in recycling. The future situation is worsened by poor recycling infrastructure and a fragmented supply chain across many parts of the globe, making it problematic to ensure a constant flow of recyclable plastic waste.
Lastly, consider public awareness and consumer behavior. A lack of knowledge about appropriate recycling practices results in a greater quantity of plastic waste being disposed of incorrectly, further complicating the recycling process. Untangling these multilayered issues will demand a global collaborative effort, breakthroughs in recycling technologies, and a reinforced framework of legislation to promote the use of recycled materials.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
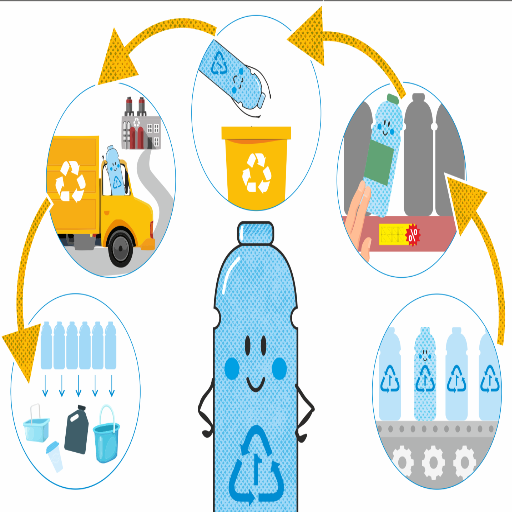
Plastic Waste and Its Consequences
Plastic waste has emerged as one of the modern-day environmental challenges with which humankind now has to contend. Approximately 7 million tons of plastic are produced globally every year, and a significant percentage ultimately ends up in landfills, waterways, and oceans. There are widespread ecological damages wrought by the occurrence of plastic in marine ecosystems, which animals swallow or become entangled in the synthetic debris. An estimated 100,000 marine mammals and millions of seabirds die every year due to plastic pollution.
Besides wreaking havoc on wildlife, this ever-growing accumulation of plastic waste poses a significant threat to the environment and humans, with far-reaching consequences. Microplastics—the tiny, broken-down pieces of plastic—are already found in the air, water, and food chain, raising concerns about their impact on human physiology. The release of greenhouse gases occurs during the production and incineration of plastic, which is adverse to climate change.
Such challenges call for a multitasking approach; however, innovative solutions and sustainable approaches will be implemented to mitigate the menace of plastic waste. These include bioplastics, better recycling infrastructure, and policy frameworks that promote a circular economy, whereby materials are reused and repurposed instead of being discarded. Hence, educating communities and helping individuals to empower themselves to make green choices stands at the forefront of this entire issue.
In Pursuance of Recycling and Reducing Plastic Waste
Strategies aimed at curbing plastic waste and improving recycling are being implemented worldwide by governments, industries, and other groups and individuals alike. Chemical recycling technologies, for example, are advanced and tested globally to decompose plastics into their original molecular building blocks, from which high-grade materials can be obtained in large quantities. Many countries, moreover, have introduced extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs that require manufacturers to take responsibility for the disposal of their products, encouraging sustainability and eco-design.
All the more so, grassroots initiatives, including plastic take-back schemes and deposit-return systems, work very well in stimulating recycling behavior. In recent times, such deposit-refund systems have achieved recycling rates “above 90%” in Germany. Meanwhile, cutting-edge solutions, such as the pyrolysis conversion of plastic into energy, are increasingly regarded as attractive alternatives to landfilling.
Educating consumers to reduce plastic waste is equally essential. Numerous campaigns support zero waste or reduced waste, emphasizing the reduction of single-use plastics. Businesses are moving towards plastic-free packaging, and customers are becoming open to alternatives to conventional packaging solutions, such as reusable options like water bottles and shopping bags. It highlights the need to consider technology, policy, and individual action, working together to tackle the menace of plastics effectively.
The Future of Plastic Pellets in Sustainable Practices
The future of plastic pellets in sustainable practices is inherently linked to continued developments in materials science and innovative recycling regimes. These small, ubiquitous building blocks form the basis of innumerable plastic products, which essentially means that their sustainable handling is of paramount importance. Researchers are supporting biodegradable and bio-based plastic pellets as alternatives to the conventional petroleum-based ones. For example, plant-based polymer pellets, such as polylactic acid (PLA), appear to hold promise in reducing environmental impact while maintaining functionality.
In addition to this, improved mechanical and chemical recycling are proving to be the key aspect of giving plastic pellets a second life. Closed-loop operations, where used plastics are converted into new pellets with minimal degradation, are becoming a practicable approach. Reducing virgin plastic production further translates into preserved resources and fewer greenhouse gas emissions. It is expected that, within the next ten years, plastic waste in industries could be reduced by 50% if such circular practices are embraced.
Policy interventions are also essential for steering the future. Many places are now set to impose regulations that will assuredly control the proper production and disposal of plastic pellets and offer a rewarding system for opting for alternatives that are better for sustainability. The direct effect of such politics will be the ecologically sound use of plastic pellets, thereby promoting economic development while fostering environmental consciousness.
Conclusion: The Future of Plastic Pellets

Trends in Plastic Pellet Usage
From my perspective, the use of plastic pellets is undergoing a dynamic evolution due to changes in technology and global priorities over time. Industry-wise trends in the sector are shifting towards innovative solutions that minimize the environmental footprint associated with pellet production and use. For instance, biodegradable and bio-based plastic pellets are becoming substitutes on the sustainability spectrum in packaging, agriculture, and consumer goods. These materials aim to create alternatives to fossil fuel-based materials while addressing the long-standing issue of waste management by presenting a more sustainable solution for the end-of-life fate of these materials.
Another aspect that is much appreciated and gaining momentum is circular economy thinking. Companies have moved towards closed-loop systems, where recycled plastic pellets can be repurposed in production, thereby reducing the use of virgin plastics. Furthermore, recent advances in recycling technologies, including chemical recycling, have significantly improved the quality of recycled plastic pellets, making them comparable in terms of performance and cost-effectiveness to virgin pellets.
Overall, in my opinion, the balance between creative approaches and regulation would make a strong case for the future of plastic pellet usage. Hence, industries would be able to satisfy economic needs while aligning with the sustainability wave in conjunction with other cutting-edge activities, carving out an accountable and future-oriented approach to handling plastic pellets.
The Importance of Recycling and Innovation
Recycling and innovation are the cornerstones of a sustainable future, particularly for materials like plastic. To me, recycling is really about waste reduction, resource conservation, and environmental protection. That is, by reusing another product or material, the demand for virgin products is significantly reduced, and less energy is used in the process, resulting in lower carbon emissions. Recycling plastic pellets, for example, helps control the spread of microplastics and thus preserves ecosystems, preventing further degradation of marine life.
Simultaneously, I believe innovation is just as crucial in addressing environmental issues. For me, investing in R&D to improve recycling technology and create advanced materials would be a significant step towards the circular economy. Innovations in production processes, degradable substitutes, and recycling technologies will enable industries to initiate or accelerate their transition to sustainable practices while maintaining competitive advantages in performance. Altogether, it is recycling and progressive innovations that create the biggest and most comprehensive solutions —a system.
The combination places us in a position where we can begin to propose solutions for the pressing environmental issues while meeting the requirements of industries. Being able to present new approaches together with a solid strength in recycling, I believe, will lead to a more responsible option for the environment. Whether through policy changes, breakthroughs in science and technology, or grassroots initiatives, recycling and innovation are always worthwhile endeavors to pursue. These two reasonable plans will help nurture the necessary changes for the Earth and future generations.
Some Final Thoughts on Plastic Pellets in Daily Life
Being small, plastic pellets have a profound impact on modern life and environmental concerns. They are the foundational bricks that constitute innumerable products we rely on today, ranging from packaging materials to electronics and medical devices. Let me see them for environmental axes too, especially as microplastics. I believe that education, innovation, and road-mapping towards accountability in the entire production and supply chain will be the key to finding an answer that manages this duality.
On the other hand, plastic pellets represent efficiency and innovation, enabling industries to develop lightweight, durable, and cost-effective solutions. However, the inappropriate handling, transportation, and disposal of pellets are among the significant causes of pollution, particularly in marine ecosystems. A step in the right direction would be for industries to implement more stringent containment measures, establish robust regulatory frameworks, and channel investment in research toward sustainable materials or alternatives.
The example of plastic pellets highlights the need to balance human progress with environmental stewardship. By changing the way we create, use, and recycle these materials, one can enable a sustainable and responsible approach. That means all of us, with focused policies, global cooperation, and individual responsibility, can ensure that the benefits of plastic pellets do not harm the health of this planet and future generations.
Reference Sources
- What are some common uses of plastic granules? – Discusses daily life applications of plastic granules in various products.
- What can plastic pellets be made into? – Explores their use in the clothing industry and other accessories.
- What are Plastic Pellets Used For? – Highlights their role in manufacturing plastic products through various processes.
- 10 Surprising Ways to Use Plastic Pellets You Didn’t Know About – Covers unique applications like weighted blankets and crafts.
- What is the role of pellets within the plastics industry? – Discusses their environmental impact and energy-efficient manufacturing.
- View PC Plastic Pellets Manufacturers in China
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What plastic products can be made from plastic pellets?
Plastic pellets, also known as nurdles, have a multitude of uses, ranging from packaging plastic goods to manufacturing plastic containers, such as water bottles for consumers, and various other automotive applications. Hence, plastic pellets can be shaped into different forms employing techniques such as injection molding and extrusion. The small granules are relied upon in the manufacturing sector to realize into various rigid, reusable items. The applications of plastic pellets range widely, encompassing everyday types of containers to specialized ones.
How are recycled plastic pellets made?
Recycled plastic pellets are made from post-consumer waste plastics that are collected and processed, thereby reducing plastic pollution. Such a recycling process usually begins with a thorough cleaning of the waste plastic. The waste plastic is then shredded and melted down into small granules that can be further used in the manufacturing of new products, thus promoting awareness and conservation of the environment. Through recycling plastic waste, the demand for virgin materials is lowered, which preserves resources and keeps the ecosystem free from contamination. The use of recycled pellets is gaining increasing acceptance in the plastic industry as companies strive to reduce their environmental footprint.
What are the advantages of plastic pellets in manufacturing?
The use of plastic pellets in manufacturing offers numerous advantages, primarily driven by efficiency and cost. Being tiny granules, they are easily moved across distances and stored, which aligns well with manufacturing procedures such as injection molding and extrusion. They are uniform in size and, therefore, guarantee their melting and shaping to form products of superior quality. Formulations of plastic pellets may differ in specific properties, such as toughness or flexibility, depending on the application’s requirements. This feature makes it widely used in several industries, including packaging and the automotive sector.
What types of containers can be made using plastic pellets?
Plastic pellets are widely used to manufacture containers for food packaging, storage, and transportation. Of these containers, those made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and polypropylene (PP) are well-known for their strength and durability. Usually, containers made of these two types of plastics are designed to be reused or recycled, thereby reducing plastic waste. Besides generic packaging, specialized containers are created for industrial applications, demonstrating the versatility that plastic pellets offer in providing specific solutions.
How do plastic pellets reduce plastic waste?
Plastic pellets play a crucial role in reducing plastic waste, serving as feedstock materials in recycling operations. When recycled plastic is formed into pellets, it becomes a valuable resource for the production of new items, thereby diverting potential waste from landfills and oceans. This way, pollution is reduced along with the mining of raw materials from the environment. Encouraging the use of recycled pellets helps establish a closed-loop system fostering sustainability and environmental responsibility. Growing awareness of recycled materials is crucial in addressing the issue of plastic pollution.
What environmental impacts occur by using virgin plastic pellets?
The environmental effects of using virgin plastic pellets can be significant due to the extraction of petrochemicals required for their production. Such activities contribute to pollution and ecological degradation, including habitat destruction and carbon emissions. Additionally, the introduction of plastic products made from virgin plastic into waste disposal sites leads to the release of plastic waste into ecosystems, harming wildlife and marine life. Not only that, but recycled plastic pellets could also incidentally mitigate these adverse effects due to their reduced demand for the production of new plastics. Addressing these environmental concerns is crucial for the future of the plastics industry.




