When heating food in the microwave, safety is paramount, especially regarding the materials you use. LDPE, or Low-Density Polyethylene, is a standard plastic used in a vast variety of food packaging, containers, and wraps. However, the question remains: Is it microwave-safe? This guide delves further into the safety issues surrounding LDPE, enabling you to understand its unique properties, how it reacts to high temperatures, and the potential risks it poses. Whether you’re working a hectic job and just want to throw some leftovers in the microwave, or you’re truly into the whole meal prep thing, it is vital to understand what goes in your microwave to look out for your own health and the quality of your food. Continue reading for everything you need to make informed decisions about safe kitchen practices.
Understanding LDPE and Its Properties

What is LDPE?
LDPE stands for low-density polyethylene and is a thermoplastic polymer commonly used for flexible, lightweight plastics. A second factor of considerable importance for LDPE is its processing temperature and high durability. Due to free-radical polymerization at high pressure, LDPE is broadly branched, making it very flexible, transparent, and water-resistant.
Its use is widespread for kitchen wraps, grocery bags, and squeeze bottles; even some milk cartons are lined with this material. It exhibits a melting point of around 221°F (105°C), which allows it to withstand moderate heat without immediately breaking down into lower-quality polymers. Prolonged exposure to higher temperatures, such as microwaving, may allow the chemicals within to leach, raising safety concerns when MDF comes into contact with food under certain conditions. This has led to extensive research and debates on the best methods for preparing and storing food using LDPE. Being familiar with the properties of LDPE would certainly aid in making informed decisions about its use for food storage or preparation.
Common Uses of LDPE in Packaging
Due to the flexibility, durability, and weather-resistant nature of LDPE, it finds a broader range of applications in packaging. Mostly, LDPE plastic bags, such as grocery bags, produce bags, and bread bags, are manufactured from it because these items need lightweight and cost-effective materials to protect their contents. It also finds application in shrink-wrapping and stretch-filming, which act as very strong and flexible means of securing products during transportation and storage.
Another great application area is the fabrication of containers and lids for food. Since LDPE has excellent barrier properties, a product can be stored and preserved from the ingress of contaminants or moisture. Another application includes the manufacture of liquid packages, such as cartons with an LDPE layer that serves as a leakage barrier and maintains structural integrity. Rubber elasticity also makes this material suitable for squeezing bottles of condiments.
From the producers’ perspective, LDPE contributes to sustainability as it is recyclable and used as recycled post-consumer content. This enables packaging manufacturers to meet the growing demand for environmentally friendly solutions that do not compromise functionality or quality. LDPE straddling practicality and green solutions has been a cornerstone in modern packaging solutions for various industries.
Physical Properties of LDPE
Low-Density Polyethylene is technically a diverse group of polymers due to its wide range of manufacturing processes. The polymer is a thermoplastic with a density range of 0.915 to 0.935 g/cm³, giving it some flexibility and toughness. It is semi-transparent with a waxy exterior, whereas LDPE finds other applications such as film packaging, coating, and molded parts.
One crucial feature of LDPE is its resistance to moisture and chemicals, allowing it to maintain its structural integrity when exposed to liquids, acids, and alkalis. It also has a low melting temperature, ranging from 105 to 115°C, making it easiest to prepare through extrusion and injection molding.
The defining features of the LDPE include its superb insulation properties against electricity. This attribute makes LDPE a perfect candidate for wire and cable insulator applications in the electrical industry. LDPE also exhibits superior resistance to impact and mechanical stress, offering increased durability in applications that experience heavy use.
These qualities, together with being lightweight and inexpensive, have contributed to its increased use in various industries, such as packaging, construction, and consumer goods, as manufacturers shift toward sustainable production.
Microwave Safety: The Basics
How Microwave Works
Microwaves contain electromagnetic waves in the microwave-frequency range that heat food by acting upon water molecules. As the food is subjected to the waves, water, fat, and sugar molecules vibrate at a high speed, producing heat due to molecular friction. This heat is used to cook the food, a method known as dielectric heating. The food is cooked evenly within, whereas in conventional ovens, the heat source is outside, and external heat simply cooks the food externally. Microwave cooking significantly reduces cooking time because it works by penetrating the surface. The moisture content of food, its density, and its size all influence how fast and evenly the food heats, so it is equally essential to portion and position food correctly in the microwave. Increasingly, microwave ovens are being engineered to include sensors to measure temperature and moisture levels, guaranteeing greater accuracy and consistent cooking results.
Why Some Plastics Are Microwave-Safe
Any type of plastic can be microwaveable, and the suitability generally depends on the chemical composition and design of the plastic. For instance, plastics considered safe for microwaves were made of either polypropylene or polyethylene, materials that resist melting, warping, or releasing dangerous chemicals at high temperatures. These plastics are designed to stay intact even under the intense heat and radiation of microwaves; as such, they do not leach toxins into food.
For a microwave to be safe, the plastic should not contain harmful chemicals that are released when heated, such as bisphenol A (BPA) or phthalates, which are typically found in older types of plastic or low-grade plastics. Today, BPA-free plastics are considered safer because they provide consumers with assurance that the toxic chemicals will not be released. Additionally, microwave-safe plastics undergo rigorous testing to ensure they conform to the safety standards of regulatory agencies, such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and present no threat to consumers.
Reading and taking heed of labeling are equally important; only containers bearing the microwave-safe symbol should be used in the microwave. Using the right plastics for reheating meals is crucial for maintaining food quality, health, and safety; therefore, it is essential to use trusted plastics that are specifically formulated for this purpose. Owing to these innovations, microwave-safe plastics are used in the kitchen for cooking and storing food.
Discerning Microwave-Safe Containers
To consider it microwave-safe, there must be markings or specific features that indicate safety standards. Microwavable containers are often made from plastics such as polypropylene or high-density polyethylene, known for their toughness and, to a slight extent, heat resistance. They tend to become warped upon microwaving and may also emit harmful fumes in some cases. Additionally, most microwave-safe containers are clearly marked with the phrase “microwave-safe” or the microwave symbol.
Another safety test is to fill the container with water, microwave it for about one minute, and check that it should stay relatively cool while the water heats. If the container itself tends to become very hot, it is most probably not microwave-safe. Do not use any container with metal elements, for such elements generate sparks or cause damage to the microwave.
Being extremely conscientious about selecting microwave-safe containers is crucial for protecting the health of users. It prolongs the life of the microwave while providing oatmeal with uniform reheating for its route to consumption. Nowadays, microwaves come with automated tools, such as plastic safety detectors, that further assist in choosing and using the proper containers. The deliberate choice of material and design makes the entire process of reheating food even smoother, essentially creating an additional layer of support for microwave-safe containers in everyday kitchen use.
The Role of BPA in Plastic Containers
What Is BPA and Why Is It Important?
BPA, or bisphenol A, is an industrial chemical that has been widely used in the making of plastics and resins. These materials can be found in everyday food containers, such as reusable water bottles and storage containers, for storing food items. It can also be found in the linings of cans. BPA has raised considerable concern in recent times due to its potential impact on human health and the environment. Scientists have stated that BPA may leak into food or beverages from containers when these containers are subjected to heat or acidic substances. BPA is an endocrine disruptor that can interfere with the hormonal balance of the body, thereby posing possible health effects such as developmental disorders, reproductive harm, or an increased risk of some cancers.
Increasing evidence supporting measures against BPA has led to the introduction of more specific regulations. Many manufacturers, therefore, are now producing BPA-free alternatives made from materials like polypropylene or Tritan plastic, which are considered safer for food-related applications. While these alternatives shield one from direct BPA exposure, the jury is still out on the hazards the alternative materials may pose in the long run. For another perspective, consumers may want to look for BPA-free labels or opt for glass or stainless steel containers to take a step toward reducing potential risks. Staying educated and making informed decisions will enable an individual and their family to be best protected against any potential side effects associated with BPA exposure.
About BPA-Free Options and Why They Matter
With increased awareness among consumers and health messages about the uncertainties surrounding bisphenol-A, the BPA-free concept has been gaining traction in the mainstream since the early 2000s. It has been demonstrated that even very low levels of BPA in the human bloodstream can affect the endocrine system; hence, the shift toward safer alternatives for potentially susceptible consumers holds paramount importance, again, pregnant ladies and children being primary considerations. Many manufacturers today advertise BPA-free products, which are made from alternative materials such as Tritan, glass, stainless steel, and food-grade silicone. Consider Tritan —an extremely tough plastic often used for water bottles and food containers, free of harmful chemicals and pesticides.
Industry reports from recent times indicate an increase in consumer buying tendencies for BPA-free items, with the global BPA-free market expected to grow at an annual rate of over 6% in the next few years. This change is evident in the ever-growing range of BPA-free options available for homeware, reusable containers, and even thermal receipts. By making BPA-free options more accessible, manufacturers empower consumers to make informed decisions about health versus convenience and functionality.
Choosing BPA-free options is also sustainable because, as alternatives, glass and stainless steel materials are more secure and recyclable with a lesser environmental toll. It provides people with alternative options to prioritize their health and support the environment while navigating life in response to ever-changing safety standards.
Observing the BPA Levels in LDPE
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) is a broadly used packaging material. This polymer is flexible, resilient, and lightweight. Although it is generally considered safer than BPA-containing materials for use, evaluating the chemical leaching potential under special conditions is beneficial. Recent studies highlight several important aspects related to BPA contamination cases involving LDPE. Notably, pure LDPE does not contain BPA; however, contamination can occur during production or through external contact with BPA-containing agents.
In their studies on LDPE at various temperatures and pH values, researchers have concluded that the migration of substances is minimal due to its low permeability, making it a suitable alternative for a multitude of food and beverage applications. However, manufacturers must also warn their consumers against prolonged exposure to extreme heat or the presence of harsh chemicals, as such conditions would raise the possibility of leaching and compromise the integrity of the material.
Strict testing and quality control measures are implemented to ensure the safety and reliability of LDPE in accordance with current safety and environmental regulations. With advances in polymer engineering, the product composition is further refined to reduce contamination risk, making it the preferred choice for sustainable, BPA-free packaging.
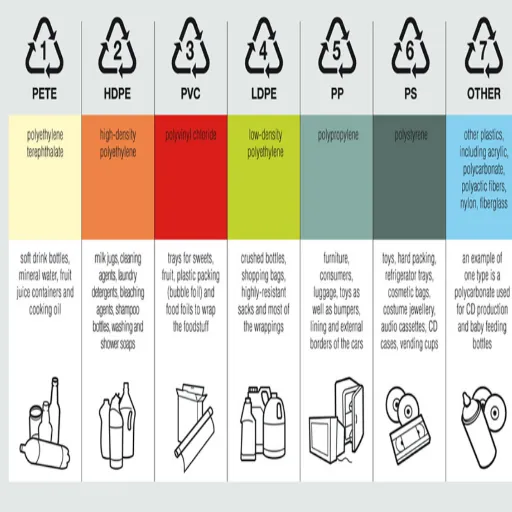
Types of Plastics: What You Should Know
Common Types of Plastics Used for Food Storage
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET or PETE)
PET is a hard plastic that is lightweight and exceptionally durable. It is thus widely imported for packaging food and sourcing water, such as in bottles, containers for salads, or jars. Its sturdiness, combined with good resistance to moisture and oxygen, helps retain the freshness of products, thus extending shelf life. It is recyclable, thereby supporting sustainability. Additionally, it is widely accredited as BPA-free for food storage applications, making it considered safer.
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
Recognized for its strength and versatility, HDPE is a preferred material in food storage applications, including milk bottles, yogurt containers, and reusable plastic bottles. It resists impact and can withstand very high or very low temperatures, does not leach harmful chemicals, and therefore will not affect the safety and quality of the food contained. HDPE is highly recyclable, which resonates with the environmentally conscious mentality.
Polypropylene (PP)
This versatile plastic type has a wide range of applications. It works really well in microwave containers, in takeout packs, and reusable food containers. This is because it is heat-resistant and tough. It also resists moisture and chemicals, thus keeping foods fresh and ensuring their safety. Such properties of PP make it lightweight while maintaining strength, which is why it is often used nowadays in modern food storage solutions.
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE)
It is a soft and flexible plastic, which is utilized in products such as plastic wraps, squeeze bottles, and bread bags, all of which take advantage of its properties. They are effective in keeping perishable food items from moisture. Over the years, improvements in the ability to recycle LDPE have made it a greener choice in food storage situations.
Polystyrene (PS)
Polystyrene is less common nowadays due to environmental concerns, yet it is still used for food packaging, including disposable cutlery, foam take-out containers, and coffee cup lids. It is, however, excellent in insulation and very convenient due to its weight; nevertheless, alternatives are being actively sought due to its lack of recyclability and lesser environmental friendliness.
By using food-grade plastics that meet stringent safety standards, food will not be contaminated and will remain fresh throughout its storage lifecycle. Choosing materials that are recyclable and free of BPA is a way for manufacturers and consumers to prioritize health, safety, and sustainability.
Comparison of LDPE with Other Plastics
| Plastic Type | Key Properties | Common Uses | Advantages vs LDPE |
|---|---|---|---|
| HDPE | High mechanical strength, chemical resistance | Pipes, heavy-duty containers | More rigid and stronger |
| PET | Excellent barrier properties, recyclable | Beverage bottles, food packaging | Better gas barrier, higher recyclability |
| PP | Temperature resistant, chemical resistant | Automotive, medical products | Higher heat resistance |
Several advantages are presented by LDPE when compared to commonly accepted alternatives, such as HDPE, PET, and PP. LDPE is flexible and resistant to impact, making it suitable for applications such as plastic bagging, shrink wrapping, and squeeze bottles, among others. Another fascinating aspect of such lightweight packaging applications is the combination of lower density and high clarity.
LDPE is an elastic and flexible polymer, wherein the rigidity and strength are opposite properties exhibited by HDPE. Hence, HDPE has enhanced mechanical strength and resistance to chemical attack, making it suitable for applications such as pipe fittings and heavy-duty containers. However, it is not as excellent as LDPE in terms of transparency and ease of processing.
PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) is yet another common alternative, particularly for beverage bottles and food packaging, owing to its excellent barrier properties and recyclability. While PET stands out in terms of durability and resistance to gas permeation, LDPE is less costly and easier to mold, and is therefore considered better for applications where flexibility outweighs stiffness.
Being similar to LDPE in terms of being lightweight, PP often surpasses it in terms of temperature and chemical resistance. While PP finds use in automotive parts, medical products, and high-heat applications, LDPE is used in single-use and disposable items due to its low melting point and ease of fabrication.
From an environmental perspective, LDPE is less recyclable than PET and HDPE, which are more widely accepted by recycling systems. The fact that LDPE is achieving research advances in its recycling, yet higher recycling rates are being attained for other plastics, underscores the need for research into alternative, more sustainable processing methods or possibly biodegradable alternatives for broader use.
Through this comparison, it is clear how LDPE, being versatile, is employed in a myriad of circumstances; however, the choice of LDPE must be based on the requirements of durability, cost, environmental impact, and processing options for optimal performance.
What are Food Grade Plastics?
Food-grade plastics are these materials that ensure the safe keeping, shipping, and consumption of food products. These plastics are prepared in accordance with stringent safety standards to ensure that they do not release any harmful chemicals or contaminants when subjected to specific conditions, such as heat or moisture. Some common examples are polyethylene terephthalate (PET), high-density polyethylene (HDPE), and polypropylene (PP). Each has different properties that make it suitable for various applications. For instance, PET is widely used for beverage bottles due to its durability and clarity, while PP is used for microwaveable containers because of its heat resistance.
Additionally, environmental consciousness has led to newer food packaging treatments through bioplastics made from renewable resources, such as cornstarch. The recycling ability and reusability of conventional food-grade plastics are also being improved, with their recyclability and lifecycle assessments now serving as key metrics for sustainability. These developments consider food safety and align with marketing needs for greener alternatives in packaging and storage.
Safe Practices for Using LDPE in the Microwave
Best Practices for Cooking in LDPE Containers
- Check for microwave-safe labels: The very first step is to check for the microwave-safe label etched on the container. Some LDPE containers may not be suitable for microwave heating; therefore, it is essential to remember this key point if you do not want to risk your plastic melting or contaminating your food with unwanted chemicals.
- Use for reheating, not cooking: Ensure that you use LDPE containers designed explicitly for reheating, rather than cooking, as exposure to higher temperatures for a longer time in the microwave can be detrimental not only to the plastic but also to the food inside.
- Allow steam to escape: Either partially open the lid or remove it and set it aside, as some microwave-safe covers allow steam to escape safely, ensuring there won’t be any buildup of pressure.
- Heat in intervals: Heating time is kept to a minimum; heat and stir the food frequently to ensure uniform heating.
- Regular inspection: Carefully clean and inspect the container after every use. Inspect LDPE plastic containers for signs of damage, such as warping or discoloration, as repeated microwaving may cause them to deteriorate. If so, replace the container.
Proper use of LDPE containers protects the user’s health and allows the containers to last longer, making them a practical and safe choice for infrequent microwaving.
Signs and Symptoms of Hazards from Using Plastics in the Microwave
Warning Signs to Watch For:
- Physical damage: Warping, cracking, or melting of containers when exposed to heat, indicating that the plastic has likely become unsafe to use.
- Discoloration: Changes in color can indicate that the material has degraded over time and chemical compounds may have started leaching into the food.
- Missing safety labels: Avoid using any plastic item that does not bear a microwave-safe label, as it may not withstand heat without breaking down or releasing harmful substances.
- Chemical odors: If a foul or chemical-like odor emanates from the microwave, this indicates that the plastic is compromising the safety of the food.
- Food type considerations: Be wary when storing and reheating fatty or oily foods, as they tend to reach much higher temperatures, thereby possibly promoting plastic degradation.
To circumvent such problems, check the containers periodically, adhere to the principle of leaving microwave-safe plastics intact, and discard any plastic that exhibits signs of wear and deterioration immediately. Upholding the safety and food quality is paramount to the responsible use of microwave-safe materials.
Alternative Microwave-Safe Options Besides LDPE
Glass Containers
Glass containers become the first choice, as they withstand high temperatures and chemical reactions without any issues regarding chemical leaching. Look for glass dishes with BPA-free plastic lids or those made of silicone. They are easier to clean and won’t lose their appearance over time, and can be taken straight from the microwave to the table.
Ceramic Containers
Ceramic is microwave-safe and adds that final touch of elegance to cooking. Ensure that the ceramics selected are labeled as microwave-safe, as anything else could be hazardous to cracking or damaging the pieces. Ceramic provides even heating and attractive presentation options.
Silicone Products
Silicone is another material to trust, especially for covers or microwaving utilities like steamers, as it’s very flexible and can withstand the highest level of heat, making it an easy option for heating or cooking.
By using such alternatives, you can reduce the potential safety hazards while promoting sustainable kitchen practices. Incorporating long-lasting materials into kitchen equipment, such as glass and ceramics, reduces the need for disposable plastics and ensures that meals can be prepared and served safely, without concerns about contamination or adverse effects on the materials. Maintaining a good balance between convenience, health, and eco-conscious alternatives is always a priority.
Reference Sources
-
What plastics can be microwaved? – US Plastic: Discusses the microwave safety of LDPE and its heat tolerance.
-
Is It Safe to Microwave My Food in Plastic? – Bennett Plastics: Explores the safety of LDPE and other plastics when used in microwaves.
-
Microwave Safe Plastics Guide – ePackage Supply: Provides insights into the safety and limitations of various plastics, including LDPE.
-
The Ultimate Guide to Food-Grade and Food-Safe Plastics – Acme Plastics: Explains the properties of food-safe plastics and their suitability for microwave use.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is microwave-safe, provided the manufacturer’s instructions are followed. However, as it can withstand somewhat moderate temperatures, it is highly recommended that LDPE containers be labeled microwave safe. Otherwise, a plastic not built for high temperatures will warp or release harmful chemicals into food. Always look for an explicit “microwave-safe” symbol on the container before using it in the microwave.
LDPE is recognized as a safer choice among plastics; however, it can release harmful chemicals at high temperatures. While it probably leaches its harmful substances less than other plastics, such as PVC and polystyrene, it’s essential to be sure of your containers – that they are meant for microwave use. Never use cracked containers to heat your food: when damaged, containers become much more prone to chemical leaching.
Microwave-safe plastic materials include polypropylene (PP) and some high-density polyethylene (HDPE) that usually carry microwave-safe markings. Always look for the microwave-safe sign on plastics to ensure they can withstand heat without melting or deforming. BPA-free plastics are also a good choice for microwave food storage, as they do not release harmful chemicals.
When using plastic food containers in the microwave, never microwave plastics that bear no microwave-safe label, as this may cause melting or warping of the plastic. Also, never microwave a container that’s cracked, and avoid containers made of polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polystyrene, or other plastics that may release harmful substances. Always follow any instructions provided by the producers, including those related to heat times and maximum temperatures, for the sake of food safety.
Be sure to use only microwave-safe containers when working with microwave food. The wrap should not be directly applied to food, as it might melt when heated or release chemicals. Do not use plastic wraps that are not intended for use in the microwave, and always follow the instructions provided for microwave-safe use to avoid hazards.
To maintain the food safety of plastic containers in the microwave, use only plastic containers labeled as microwave-safe. The microwave-safe symbol should be looked for, or one can check recycling codes to determine the plastic type. Containers that are cracked or made of harmful plastics, such as polycarbonate, should never be used, as they may contain BPA. Adhering to the manufacturer’s instructions for heating times and usage in direct contact with food also helps to guarantee food safety.