In food microwaving, safety is always ROI 1 for the food being microwaved and the container used. There are too many plastics that go in kitchens to make it imperative to identify those that are safe for microwave use and those that are harmful. PS6, a type of polystyrene plastic, often appears in disposable dinnerware—and is a hot topic in the debate about its safety. Can you innocently pop your PS6 container into the microwave, or has some danger lurked behind it that you should recognize? This guide aims to unravel that mystery so you can understand what makes PS6 good or bad, potential hazards, and best practices for a worry-free food-heating operation. Gather information that ensures an informed decision, protecting your health and home.
Understanding Microwave Safety
What Does Microwave Safe Mean?
The term “microwave safe” refers to anything that does not break down, melt, or leach chemicals into your food when exposed to the conditions of a microwave oven. Being microwave-safe means the materials can withstand the high temperatures and electromagnetic radiation to remain stable during use. For instance, glassware, ceramic ware, and certain plastics have been strictly tested to ensure their safety for use in reheating or cooking.
With plastic containers, one has to check; identifying a container as microwave-safe means knowing which resin identification code is on the container bottom. These codes indicate the type of plastic and its heat tolerance. For instance, plastics bearing code #5 are theoretically safer to microwave, as polypropylene is heat-resistant and less likely to leach chemicals. If plastic with code #6 is subjected to high heat, it might start to melt, becoming a health hazard.
Ultimately, such items may be welded with their microwave-safe label or symbol for ease of checking. Always, when in doubt, stick to the manufacturer’s directions and use alternatives like glass or ceramic for safer, more dependable heating.
Types of Microwave Safe Containers
Glass Containers
Microwave glassware is the best choice, as it is non-porous, heat-resistant, and does not emit hazardous chemicals at superheated temperatures. Usually, borosilicate glass is a good choice because it withstands sudden temperature changes, minimizing the risk of cracking or breaking. Also, always make sure the container is marked “microwave safe,” if it does have one.
Ceramic Containers
Ceramic plates and bowls are considered microwave-safe and are a favorite because they are durable and evenly distribute heat. Steer away from ceramics with metallic finishes or decorations, as they can cause sparks or damage the microwave.
Microwave-safe Plastics
The primary category comprises plastics used for microwave cooking and heated with food. Such plastics resist heat, reducing the risk of chemical leaching into food. They might come in the form of a polyethylene bag, polypropylene box, edible wax paper, or the like. The marking of microwave safe is utmost important before any food operation. Never use any plastics that are warped, brittle, or damaged for sure.
Silicone Containers
Perfect for the microwave, they are best made from food-grade silicone. Flexible and lightweight, this option is increasingly becoming popular. These containers are heat-resistant and do not contain chemicals such as BPA. They are suitable for reheating or steaming, as they do not deform at high heat.
Paper-based Products
For short reheating jobs, microwave-safe paper plates, napkins, and parchment paper are usually suitable. Do not use printed or coated paper products, as the inks or finishes may not be heat-resistant and can emit toxins or melt when heated.
Using the right microwave-safe container promotes even heating of food and protects against potential hazards like chemical contamination or accidents. Give utmost importance to containers that meet safety standards and are certified “microwave-safe.”
How to Detect Safe Containers for Microwave Use
When checking whether a container is safe for microwaving, look for a label or mark that condemns or indicates such an endorsement. Most microwave-safe containers should have a symbol, such as wavy lines or text that reads “microwave safe.” Furthermore, glass, ceramic, and plastic materials that resist heat deformation will be your best bets. Make sure to use a plastic container with recycle codes 1, 2, 4, and 5, as these are less likely to release harmful chemicals when heated.
🔬 The One-Minute Microwave Test
- Put the container in the microwave with a cup of water
- Microwave for one minute
- If the container stays cool while the water heats, it is indeed microwave-safe
- If it feels hot, it may not be microwave-safe
⚠️ Polystyrene containers (recycling code 6) and unmarked plastics should never be used, as we sometimes risk chemical leaching or melting. Following these guidelines ensures microwaving is done safely, for food quality and health.
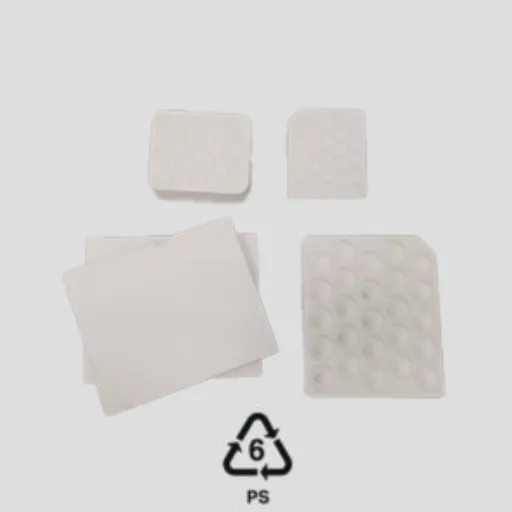
Exploring PS6 Plastic
What is PS6 Plastic?
PS6 plastic, or polystyrene, is a thermoplastic with diverse properties that can be easily manipulated in the laboratory, depending on molecular weight, and is used in many processes and applications, such as bathing processes with large equipment. It mainly comes in two forms: solid polystyrene and EPS. Solid polystyrene is often found in disposable cutlery or CD cases, as well as in plastic models; whereas EPS is used in packaging, insulation, food containers like disposable coffee cups, and takeaway boxes. Despite being very cheap and convenient, polystyrene cannot be biodegraded and poses a serious threat in terms of the environment. Due to properties such as lightweight and low secondhand market demand, recycling is really unviable in most areas, thus posing accumulation problems in landfills beyond capacity. Polystyrene also has some drawbacks: heating or degradation processes may release chemicals like styrene, which has always sparked health debates. Knowing more about its nature and effects helps individuals and firms make wise choices about its use or disposal.
Polystyrene: Properties and Uses
Polystyrene is a multifaceted synthetic polymer that is formed by the condensation of styrene monomers. It is lightweight, rigid, and insulating. It is used chiefly in two forms—one as a solid sheet and the other as foam. The solid variety is used in products that require a certain degree of rigidity, such as disposable cutlery, CD cases, and food trays. The foamed variety, known commonly as expanded polystyrene (EPS), is widely known for its thermal insulation and shock-absorbing properties. EPS can be used to make packaging materials, building insulation, and protective cushioning for delicate items.
Its affordability and manufacturing ease have established polystyrene as an option widely used in several sectors such as construction and consumer goods. For instance, EPS has become a coveted insulation material for energy-efficient building systems. In food service, it is primarily used for single-use items such as cups, trays, and containers that efficiently maintain the temperature of food and beverages. The environmental impact of these raw materials has, however, necessitated an ongoing search for sustainable alternatives or at least better recycling methods that would thereby limit waste and pollution.
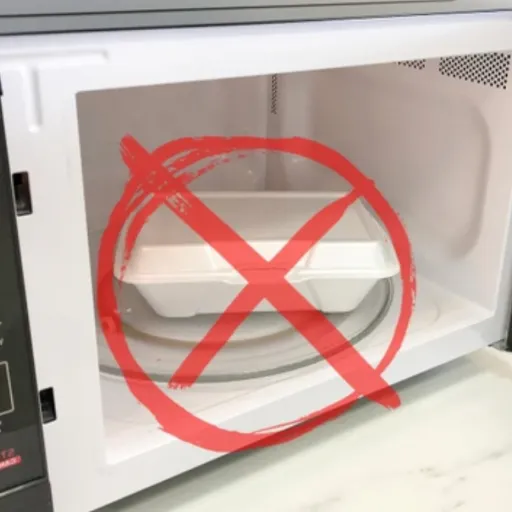
⚠️ Can PS6 Plastic Be Safely Heated in a Microwave?
Lightweight and insulating, polystyrene, or PS-6, plastic is commonly used to make various disposables, such as food containers and cutlery. But with microwaves, one has to be careful. Exposure to elevated temperatures may cause PS-6 plastic to release hazardous chemicals, such as styrene, a possible human carcinogen. The risks intensify with longer heating times or when greasy or highly fatty foods are heated, since the heat itself can degrade the material, thereby encouraging its leaching.
✅ Always ask for a “microwave safe” label. If the label is missing, the safest option is to transfer the food to a microwave-safe glass or ceramic container. Apart from being health-related alternatives, these considerations also help reduce the various environmental concerns associated with the use of polystyrene.
Microwaving Styrofoam Containers
Can Styrofoam Containers Be Put in the Microwave?
Microwaving Styrofoam containers depends on the material they’re made of. Under traditional conditions, Styrofoam, or expanded polystyrene, is generally deemed unsafe for microwave use because it cannot withstand the heat. When heated, this material will melt or warp, and some may even emit dangerous chemicals into the food, which can be harmful to human health.
On the other hand, some microwave-safe styrofoam products are made of enhanced materials that can withstand short heating periods. These products are clearly labeled “microwave-safe” after rigorous testing to ensure they remain safe and do not leach chemicals. It is highly advised to follow the heating instructions provided with these containers, as prolonged exposure to heat may still degrade their integrity.
💡 If good practice is to be followed, the recommendation states not to heat Styrofoam unless it carries a label stating “safe for microwave use.” Glass or ceramic containers are definitely the best alternatives to use while reheating food, given that these are passive materials that do not react with the substances inside them and have been designed to be used for heating purposes many times. By opting for proper containers, people can therefore put health and food safety in the forefront of their considerations during meal preparation.
Health Hazards of Heating Styrofoam in a Microwave
Styrofoam poses multiple hazards when microwaved, primarily due to the chemicals used in its production and its materials’ reactivity to heat. It is made of polystyrene, a kind of plastic that softens on exposure to high temperatures or worse, can release harmful chemicals. These chemicals may leach into food or drink in microwaves, namely styrene and benzene, both recognized as hazardous and probably carcinogenic upon prolonged exposure. More expressly, all Styrofoam items are not microwave safe. They can melt, creating a big mess that could compromise food quality or be accidentally ingested by the user.
Plastic or Styrofoam has many downsides from an environmental perspective. Even in tiny slivers, Styrofoam does not biodegrade and greatly contributes to global plastic pollution. Microwave safer options—likely to be glass or BPA-free plastics—lay off these perils while encouraging safer, sustainable practices in food prep.
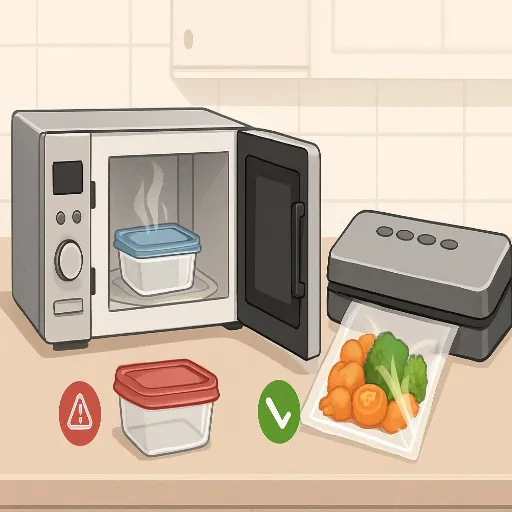
🌟 Microwaving Alternatives to Styrofoam
A plethora of alternatives exist that offer safer, more durable microwaving options, thereby reducing potential health hazards and environmental pressure. The best alternatives are made of glass, including borosilicate glass, as glass containers are nontoxic, heat-resistant, and do not leach chemicals into the food they store. Also, many glass containers are fitted with airtight, microwave-safe lids, perfect for reheating and storing food.
- Glass Containers: Another reliable choice would be microwave-safe ceramic dishes. Ceramics are perfect for heat retention and are easily cleaned, without absorbing odors or stains. Be sure to note a label indicating a product is microwave-safe to avoid cracking or damage.
- BPA-free Plastic Containers: This plastic is designed to withstand microwave heating and will not release any harmful chemicals when used properly. These are available everywhere and affordably priced for everyday use.
- Silicone Containment: The use of silicone containment has since soared due to their flexible, nontoxic, and heat-resistant characteristics. They are Microwave safe and foldable, making storage a bit easier. Moreover, these silicone bowls and lids are versatile for steaming or reheating.
One can highlight that the said alternatives set more natural limits on exposure to toxins, thereby promoting sustainable living. Microwave-safe alternatives also reduce landfill waste and are generally safer for preparing food.
Types of Plastics and Their Microwave Safety
High-Density Polyethylene and Its Safety
Commonly known as a general-purpose plastic, HDPE is durable and impact-resistant. Containers for items such as milk, detergents, and other food storage products are made from HDPE. Sometimes it is called a #2 plastic. Due to its heat-resistant, chemically stable nature, it is used across many industries. For microwave considerations, HDPE is often considered a safe material, but only if the containers are explicitly identified as such by the manufacturer. Otherwise, it identifies products that have indeed undergone testing to remain heat-resistant without releasing harmful chemicals or deteriorating.
⚠️ HDPE is considered safe for food contact, but prolonged exposure to high heat can cause gradual deterioration. HDPE can develop micro-tears from repeated heating cycles or become weakened to the point that leaching could become a concern. Along these lines, users should follow the temperature guidelines and ensure the HDPE containers they use are neither damaged nor excessively scratched. With these measures in hand, one can be assured of a healthy, sustainable way to conserve or reheat food.
Polypropylene versus Styrofoam: Which One is Safer?
| Material | Safety Profile | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Polypropylene | Sturdy, heat-resistant, very low chances of leaching harmful chemicals when exposed to heat. Heat-endurance allows microwave use. | Recyclable in many countries, making it environmentally friendly |
| Styrofoam | Releases potentially toxic substances like styrene, especially when heated or in contact with acidic foods | Non-biodegradable, adds to plastic pollution, one of the most challenging materials to recycle |
✅ When the safety of polypropylene and Styrofoam for food storage and the environment is being compared, polypropylene usually gains favor. Polypropylene is a safer enabler, thanks to its robust chemical stability and heat resistance. While it performs well in some applications, Styrofoam’s limitations make polypropylene a better all-around solution for the benefit of individuals and the environment.
About Polyethylene Terephthalate in Microwaving
PET is a polymer widely used in food and drink packaging from water bottles to microwaveable containers. It is favored for its durability, light weight, and strong resistance to microbial growth, which helps maintain food quality. But when microwaving, understanding the material’s limitations and safe practices is key.
PET containers labeled “microwave-safe” are designed to withstand high temperatures without degrading or releasing harmful chemicals. Testing on these containers is strict to ensure they meet safety standards and that they will not leach any compounds, such as antimony or phthalates, into the food being heated in the container. However, with repeated or prolonged exposure to high temperatures, the integrity of PET can be compromised; therefore, one should consider regularly replacing the containers or using them only for the intended purpose.
💡 The proper manner of microwaving, such as venting the container or avoiding overheating, is just as good in preserving the quality of the food. Learn what a PET product’s specific labeling says to ensure that health and convenience go hand in hand, making PET a good microwave choice when used cautiously.
Best Practices for Heating Food in Microwaves
Heating Food in Plastic Containers
When heating food, I always check whether a plastic container has a microwave-safe label. This is an important step because not all plastic resists high temperatures, and when heated, they can release harmful chemicals such as BPA or phthalates. Most microwave-safe containers carry a special symbol, reassuring one that they have been tested for their safety. If I have the slightest doubt about the safety of a container, I never use it in the microwave.
Another habit I found to be important is using vented lids or covering the container with a microwave-safe material such as paper towel or wax paper, thereby allowing steam to escape. Heat and pressure trapped inside can warp the lids and sometimes even cause them to pop off. I also avoid overheating; high temperatures can degrade plastics, even if the container is “safe.” Instead, I heat food in short intervals and stir it between heatings for even warmth and decreased time that the plastic is heated.
⚠️ Finally, I have learned to avoid microwaving food in old, cracked, or scarred plastics, as these imperfections create crevices where bacteria can grow while simultaneously degrading the plastic, increasing the risk of chemical leaching into food. Whenever possible, I go for glass or ceramic alternatives for frequent microwave use, which tend to be far more durable and avoid safety concerns. By heating food safely using these simple methods, I maintain the best quality in my meals and my health.
Tips for Safe Microwaving of Different Food Types
Watching various food materials heat in the microwave has led me to conclude that considering the specific properties of each food helps ensure even heating and safety. For instance, with reheated leftovers, I always spread the food out on the plate in a very thin, even layer to prevent uneven heating and cold spots where bacteria may survive. For films that are thicker or denser, I sometimes stop, stir, and continue microwaving to allow uniform heat distribution. I also usually cover my food with either a microwave-safe plastic lid or a damp paper towel that traps some steam, preventing the food from drying out and helping with even cooking.
Some foods —for example, eggs or sauces —can make a big mess when microwaved, unless you take extra precautions to avoid splattering. Therefore, I go in and pierce things like egg yolks to prevent those exploding messes. I also microwave the sauce or soup in short intervals, stirring between each to maintain a consistent temperature and avoid those annoying hot spots. I always defrost frozen items first, going slowly with the defrosting setting, instead of microwaving fast and quick. Doing so prevents parts of the item from remaining frozen while other parts are already burned. And from my experience, letting the food stand for another minute or two helps let the residual heat charge on and gets everything really warm in the process.
🍼 All in all, some mindfulness makes safe microwaving. For example, I never microwave baby food or formula in the plastic container, since hotspots may burn an infant’s tender mouth. I always transfer the baby food or formula to a glass container and test the temperature on my wrist before serving. Through such kitchen skills learned for various foods, I know my food is safe, tasty, and evenly microwaved.
Danger Signs in an Unsafe Container During Microwaving
Based on experience and research, clear signs indicate that a container may be unsafe for microwaving. One of the most common indications is that the container becomes excessively hot to the touch after only 2 minutes in the microwave. This happens with materials that are poor conductors of heat, and this situation is not only hazardous from a safety standpoint, but it may also indicate that the container is leaching harmful chemicals into your food. Another, more definable sign is if the container shows warping, melting, or cracking during or after microwaving, strongly indicating that it is not suited for such high-heat conditions.
🚨 Warning Signs to Watch For:
- Excessive Heat: Container becomes too hot to touch after short heating
- Physical Changes: Warping, melting, or cracking of the container
- Discoloration: Container changes color during heating
- Strange Odors: Unusual smells emanating from the container
- Metallic Details: Any metallic trims or decorations that can spark
- Missing Labels: No microwave-safe symbols or markings
Another red flag to watch for is the discoloration or strange smells that may emanate from a container as it is being microwaved. Both serve as signals that the material is breaking down, especially in some plastics that can emit toxic substances when heated. I also avoid containers with metallic detailing or trims, as these can spark and potentially damage the microwave. Certain labels and markings on the containers will also be clues: I make sure to look for microwave-safe symbols or heat-usage disclaimers. If the container doesn’t have any, then I usually refrain from using it.
💡 Lastly, I’ve learned to be cautious about using older or damaged containers. With time, wear and tear can compromise the material’s integrity, even if it was originally microwave-safe. Those tiny cracks or scratches, which are hardly visible, cause a transfer of harmful chemicals into food with heat. The mere act of being alert and looking for containers labeled microwave-safe will give me the safety and peace of mind I need when I reheat or cook food.
📚 Reference Sources
- Is PS 6 Plastic Microwave Safe? Everything You Need to Know – Plastic Pellet
- Microwave Safe Plastics Guide: Which Types Are Safe – ePackageSupply
- How to Identify Microwave Safe Plastics and Avoid Health Risks – Honokage
- I Ate Microwaved Food from a PP(5) and PS(6) Container – Quora
- Is It Safe to Microwave My Food in Plastic? – Bennett Plastics
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is PS6 plastic microwave-safe?
Also known as polystyrene, PS6 plastics include food packaging materials that are generally not considered safe for microwaving. Higher temperatures during microwave cooking may cause chemicals to leach from styrene into the food, raising concerns about hazardous chemicals. It is better to use containers specifically designed to be microwave-safe, such as polypropylene or HDPE.
Is it possible to microwave certain plastics in styrofoam containers?
Styrofoam containers in microwaves are not recommended. Styrofoam containers may warp under heat and release toxic fumes. It would be best if you used glass or ceramic containers that are microwave-safe. And yes, if your container has a microwave-safe symbol on it, it’s safe to use in the microwave, so always use the containers that carry this symbol.
What are the health hazards of microwaving food in styrofoam containers?
When heating food in styrofoam containers, it is advisable to put into consideration the dangers of some harmful chemicals being leached from the container into the food. Usually, these containers may not withstand high temperatures, become deformed, and also may contaminate the food. The Food and Drug Administration provides guidelines on safe food-contact materials and recommends using food containers approved for heating. Thus, to ensure food safety, it is always better to transfer your food into glass or ceramic containers.
What does the microwave-safe symbol mean?
Microwave-safe containers are designed so that they will not release harmful substances or warp when placed in a microwave oven, a significant symbol for food safety. Containers made of polypropylene, high-density polyethylene, etc., usually bear the microwave-safe labels. You must look for it when selecting microwave-safe food storage containers.
Are there microwave-safe plastic alternatives?
Yes, there are a few microwave-safe plastic options that can safely heat food. Polypropylene is among the safest plastics for microwave use, as it does not release harmful chemicals into food when heated. Also, look for containers that have been tested for safety and labeled microwave-safe. Always check the recycling code to determine which plastic products are safe to microwave.
Are disposable plastic containers suitable for reheating food in general?
One would rarely, if ever, heat food in any disposable plastic container unless the packaging clearly stated that the container was microwave safe. Most disposable containers use materials that cannot withstand microwave temperatures; thus, they will deform and release contaminants. It is best to place your food in a microwave-safe container made of glass or high-grade plastic when reheating. Check labels. Food safety should never be compromised.








